- 50% SALE
- Dental
- Midwifery
- New Products
- VOLK/OCULAR LENSES
- Anatomical Models
- Birth Sets, Dolls & Pelvis
- Brains and Heads
- Circulation
- Digestion
- Ears and Senses
- Excretion
- Eyes
- Hands and Feet
- Heart
- Individual Bones
- Infections and Illnesses
- Larynx
- Mammary Gland
- Muscular Models
- Nails
- Nerve Models
- Obstetrics
- Pelvis Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Respiration
- Skeletons
- Skin
- Spinal Cord
- Teeth and Jaws
- Torsos
- COVID
- Budget Models
- Charts & AV
- Manual Handling
- Medical Models
- Medical Simulators
- Osteology
- Veterinary
- Plant & Animal
Orchidometer - Prader
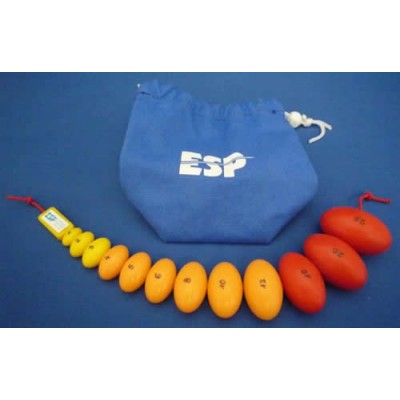
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true puberty, one of the most common uses is as a confirmation that puberty is beginning in a boy with delay. Large testes (macroorchidism) can be a clue to one of the most common causes of mental retardation, fragile X syndrome.
"Every endocrinologist should have an orchidometer - it's his stethoscope"
The Prader Orchidometer is an instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles. It consists of a chain of 12 numbered beads of increasing size from 1 to 25 ml.
The beads are compared with the testicles of the patient and the volume is read off the bead which matches most closely in size. Pre-pubertal sizes (yellow) are 1 to 3 ml, pubertal sizes are 4 to 12 ml (orange) and adult sizes are 15 to 25 ml (red).
Discrepancy of testicular size with other parameters of maturation can be an important clue to various diseases . Small testes can indicate either primary or secondary hypogonadism. Testicular size can help distinguish between different types of precocious puberty. Since testicular growth is typically the first physical sign of true pubert